CarEdge saved me over 4,500 dollars on a brand new Honda Pilot. I can't say thank you enough.
Price intelligence
Find a wide range of vehicle listings with market insights on new and used listings near you.

Help us personalize your CarEdge experience — it only takes a second.
Your answers help us personalize your CarEdge journey — we’ll follow up with tips and next steps that match your buying timeline.

If you’re planning to buy a new car, it’s important to consider the depreciation rate of the vehicle you’re interested in. Depreciation is the loss of value that occurs over time, and some cars lose their value faster than others. At CarEdge, we’ve analyzed millions of car listings and other automotive data points to provide you with proven data on the cars, SUVs, and trucks with the worst resale value in 2023. Don’t forget to check out the models and brands with the best resale value.
73.74% resale value after 5 years
After 5 years, Buick vehicles lose around 26% of their original value, making them one of the worst brands for resale value. The Buick Encore and Enclave are among the worst models for resale value, with both retaining only around 74% of their original value after 5 years.
Here’s a 2020 Buick Enclave that has lost 44% of its original value in less than three years. On top of that, it’s been sitting on the lot for 112 days. High depreciation can be a huge benefit to used car buyers. This Buick is highly negotiable.

See days on the market, local supply, negotiability score, suggested offer and more for every new and used vehicle listing with CarEdge Data.
74.06% resale value after 5 years
With a resale value of only 74.06% after 5 years, Chrysler is among the worst brands for retaining value. The Chrysler 300 is one of the worst models for resale value, with only around 74% of its original value retained after 5 years.
This 2020 Chrysler Voyager sold for nearly $10,000 more just a few years ago. However, due to ongoing minivan shortages, it’s still tough to negotiate. Days’ supply remains below average for most vans.

75.60% resale value after 5 years
Ram trucks have a resale value of only 75.60% after 5 years, making them a poor choice for those concerned about retaining value. The Ram 1500 is one of the worst models for resale value, with only around 75% of its original value retained after 5 years.
Ram can’t sell trucks right now. In fact, Ford and GM can’t either. We recently took a close look at the oversupply of trucks in America. It’s a startling contrast with the shortage of affordable new car models. Depreciation is definitely something to consider when buying a new Ram truck. This 5-year old Ram 1500 Limited with a clean record and 97,000 miles on the odometer has lost 42% of its value already.

See days’ supply, negotiability scores and recommended offers for every new and used car on the market at CarEdge Car Search.
75.77% resale value after 5 years
After 5 years, Jeep vehicles lose around 24% of their original value, putting them among the worst brands for resale value. The Jeep Grand Cherokee and Cherokee are among the worst models for resale value, with both retaining only around 72% of their original value after 5 years.
This 2020 Jeep Grand Cherokee with a clean record and just 42,000 miles on the odometer has lost 30% of its original value in three years. It’s negotiable!

77.84% resale value after 5 years
Nissan vehicles have a resale value of only 77.84% after 5 years, making them one of the worst brands for retaining value. The Nissan Armada and LEAF are among the worst models for resale value, with both retaining only around 68% of their original value after 5 years.
This 2018 Nissan Altima SR lost 32% of its value in 5 years, and that’s with a clean record and low mileage for a vehicle of that age.

Crunch the numbers with this car depreciation calculator.
Of the more than 400 models on sale in North America, these are the 20 with the highest depreciation, and the quickest to lose resale value.
| Model | 5-Year Depreciation |
|---|---|
| GMC Yukon XL | 68.38% |
| Nissan Armada | 68.80% |
| GMC Sierra 2500HD | 71.30% |
| Chevrolet Suburban | 71.86% |
| Jeep Cherokee | 72.28% |
| Kia Sorento | 72.48% |
| Nissan LEAF | 72.55% |
| Jeep Grand Cherokee | 72.70% |
| Ford Escape | 73.00% |
| Chevrolet Tahoe | 73.12% |
| Buick Enclave | 73.21% |
| Ford Expedition | 73.35% |
| Nissan Altima | 73.90% |
| Nissan Titan | 74.04% |
| Chrysler 300 | 74.06% |
| Buick Encore | 74.26% |
| Chevrolet Spark | 74.62% |
| Nissan Maxima | 75.00% |
| GMC Yukon | 75.31% |
| Ram 1500 | 75.60% |

As you can see, some models lose more than 30% of their value after just five years. Buying a car with a low resale value can cost you thousands of dollars in the long run. This is especially true if you are likely to sell your car within the next decade. So, before you make a purchase, be sure to research the resale value of the vehicle you’re interested in.
Compare depreciation between models, all in one spot.
At CarEdge, we provide you with the data you need to make informed decisions. With CarEdge Data, you can access valuable market data, including Black Book valuations, CarEdge Suggested Offer, Negotiability Score, CarEdge Recommendation, and local Days Supply in your region. With this information, you can negotiate better deals and avoid being taken advantage of by car dealerships.
Don’t get caught off guard with high depreciation. Unlock behind-the-scenes insights that will inform your car buying decisions today. And if you’re looking for 1:1 help with your deal, partner with a car buying pro with years of experience with CarEdge Coach. We’re real people helping drivers everywhere save real money. Check out these uplifting success stories to see how much you could save!

Heading into this summer car buying season, patience will reward shoppers with savings. However, a closer look at market data reveals a shocking reality: deals are very hit-or-miss in 2023. Frankly, your likelihood of buying a new car under MSRP depends on what exactly you’re shopping for. On top of that, notable differences exist between regional markets. To bring much-needed clarity to the car market in 2023, we’re sharing the latest analysis from CarEdge Data. Let’s dive in.
Among the metrics employed to track the new car market, days’ supply is one of the most widely-used. Through the industry’s ups and downs from 2020 through the present, this data point was the bellwether at every turn. But what exactly is days’ supply, and how is it calculated?
Days’ supply is a calculation used in the automotive industry to determine how long it would take for dealerships to sell their current inventory of vehicles based on the average daily sales rate. It is calculated by dividing the number of vehicles in inventory by the average daily sales rate over a certain period of time.
Here’s the car buyer’s guide to auto sales jargon and terms to know.
Historically, a 60 days’ supply is considered normal or average in the auto industry. As we’re about to see, few of the top-selling models in America are anywhere near normal heading into summer.
Are you in the market for a new truck in 2023? We have good news for you. There’s a huge oversupply of trucks in most markets as demand for overpriced inventory dried up earlier this year. Dealers are holding on to their trucks for too long, and with high floorplanning costs, they’re paying the price.
Car dealer floorplanning costs refer to the interest charges that car dealerships incur when they finance their inventory with a line of credit from a bank or a finance company. Essentially, the dealership uses the line of credit to purchase new cars from the manufacturer, and then pays interest on the loan until the cars are sold to customers. The longer the cars sit on the lot unsold, the more interest the dealer has to pay. This is why it’s important for dealers to move their inventory quickly and efficiently.
We’re seeing truck prices steadily drop in most markets. Check out these examples from CarEdge Car Search. This brand-new Ford F-150 on sale in the Dallas area has had no fewer than four price adjustments in the past few months, yet it remains on the lot after 290 days. The CarEdge Negotiability Score takes into account days on market, local supply, and other factors to give this F-150 a 97/100. The dealer is EXTREMELY likely to negotiate.
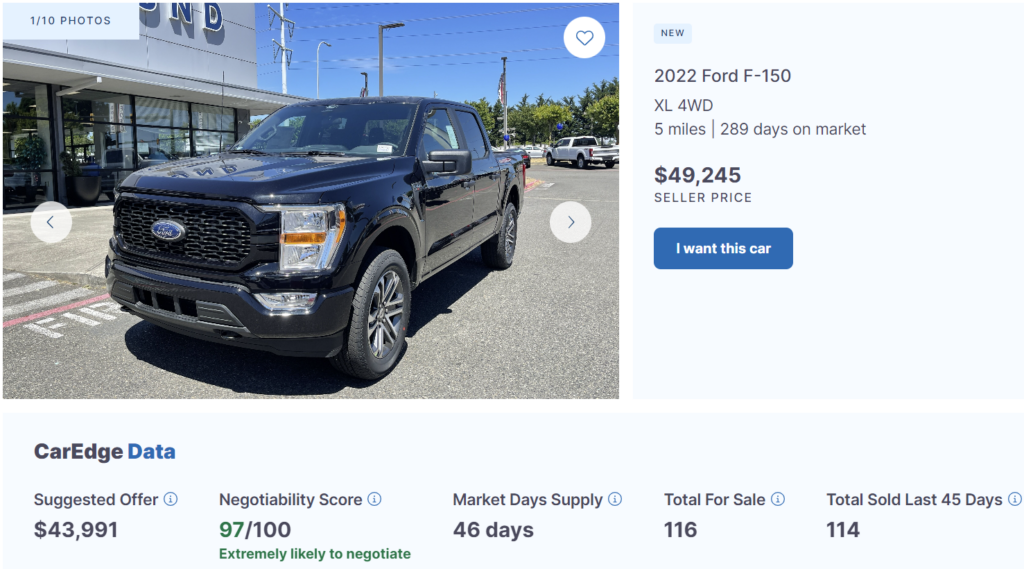
This new Ram 1500 on sale near Houston, Texas has been on sale for over 285 days. The dealer has been dreading dropping the price, but seems to have finally given in recently. This is the perfect example of a new truck that would be quite negotiable.
Affordable SUVs and Sedans In Short Supply

Is it any surprise that automakers are making more of their higher margin, expensive models and far fewer of the budget models that most drivers want? The best-selling affordable vehicles all have days’ supply well under the 60 day norm in major markets.
This includes the following best-sellers:
Let’s take a closer look at current new car inventory for the 20 best-selling cars, trucks and SUVs last year. We analyzed inventory in the five largest car markets in the United States. The following data is as-of Apr 26, 2023.
| Make/Model | Total For Sale | # Sold - 45 Days | Days Supply |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford F-150 XLT Hybrid | 515 | 138 | 168 |
| Chevrolet Silverado LT 4WD | 1092 | 276 | 178 |
| Ram 1500 Big Horn/Lone Star | 1182 | 250 | 213 |
| Toyota RAV4 XLE Premium | 543 | 876 | 28 |
| Toyota Camry LE FWD | 509 | 625 | 37 |
| GMC Sierra Elevation 4WD | 508 | 133 | 172 |
| Honda CR-V Sport FWD | 361 | 968 | 17 |
| Toyota Tacoma TRD Off Road 4WD | 490 | 505 | 44 |
| Tesla Model Y Long Range (used - 2021) | 110 | 23 | 215 |
| Jeep Grand Cherokee Limited 4WD | 328 | 412 | 36 |
| Toyota Highlander XLE FWD | 1114 | 1692 | 30 |
| Toyota Corolla LE | 767 | 829 | 42 |
| Chevrolet Equinox LS | 390 | 181 | 97 |
| Ford Explorer XLT | 1375 | 364 | 170 |
| Tesla Model 3 RWD (used - 2021) | 118 | 20 | 266 |
| Nissan Rogue SV | 1481 | 1443 | 46 |
| Jeep Wrangler Unlimited | 506 | 107 | 213 |
| Hyundai Tucson SEL | 1365 | 1387 | 44 |
| Subaru Crosstrek Limited | 300 | 754 | 18 |
| Honda Accord EX | 790 | 617 | 58 |
| Make/Model | Total For Sale | # Sold - 45 Days | Days Supply |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford F-150 XLT Hybrid | 832 | 267 | 140 |
| Chevrolet Silverado LT 4WD | 890 | 253 | 158 |
| Ram 1500 Big Horn/Lone Star | 908 | 118 | 346 |
| Toyota RAV4 XLE Premium | 1003 | 1142 | 40 |
| Toyota Camry LE FWD | 621 | 683 | 41 |
| GMC Sierra Elevation 4WD | 388 | 206 | 85 |
| Honda CR-V Sport FWD | 1052 | 1028 | 46 |
| Toyota Tacoma TRD Off Road 4WD | 585 | 1737 | 15 |
| Tesla Model Y Long Range (used - 2021) | 82 | 51 | 72 |
| Jeep Grand Cherokee Limited 4WD | 182 | 103 | 80 |
| Toyota Highlander XLE FWD | 357 | 766 | 21 |
| Toyota Corolla LE | 642 | 950 | 30 |
| Chevrolet Equinox LS | 301 | 122 | 111 |
| Ford Explorer XLT | 627 | 198 | 143 |
| Tesla Model 3 RWD (used - 2021) | 63 | 74 | 38 |
| Nissan Rogue SV | 754 | 650 | 52 |
| Jeep Wrangler Unlimited | 217 | 103 | 95 |
| Hyundai Tucson SEL | 284 | 419 | 31 |
| Subaru Crosstrek Limited | 8 | 139 | 3 |
| Honda Accord EX | 1020 | 516 | 89 |
| Make/Model | Total For Sale | # Sold - 45 Days | Days Supply |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford F-150 XLT Hybrid | 479 | 211 | 102 |
| Chevrolet Silverado LT 4WD | 546 | 150 | 164 |
| Ram 1500 Big Horn/Lone Star | 469 | 66 | 320 |
| Toyota RAV4 XLE Premium | 198 | 432 | 21 |
| Toyota Camry LE FWD | 113 | 156 | 33 |
| GMC Sierra Elevation 4WD | 167 | 69 | 109 |
| Honda CR-V Sport FWD | 125 | 380 | 15 |
| Toyota Tacoma TRD Off Road 4WD | 289 | 324 | 40 |
| Tesla Model Y Long Range (used - 2021) | 29 | 20 | 65 |
| Jeep Grand Cherokee Limited 4WD | 173 | 119 | 65 |
| Toyota Highlander XLE FWD | 303 | 637 | 21 |
| Toyota Corolla LE | 214 | 241 | 40 |
| Chevrolet Equinox LS | 131 | 203 | 29 |
| Ford Explorer XLT | 572 | 126 | 204 |
| Tesla Model 3 RWD (used - 2021) | 11 | 17 | 29 |
| Nissan Rogue SV | 482 | 405 | 54 |
| Jeep Wrangler Unlimited | 115 | 31 | 167 |
| Hyundai Tucson SEL | 528 | 598 | 40 |
| Subaru Crosstrek Limited | 33 | 229 | 6 |
| Honda Accord EX | 188 | 185 | 46 |
| Make/Model | Total For Sale | # Sold - 45 Days | Days Supply |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford F-150 XLT Hybrid | 1269 | 301 | 190 |
| Chevrolet Silverado LT 4WD | 918 | 176 | 235 |
| Ram 1500 Big Horn/Lone Star | 832 | 140 | 267 |
| Toyota RAV4 XLE Premium | 134 | 229 | 26 |
| Toyota Camry LE FWD | 122 | 199 | 28 |
| GMC Sierra Elevation 4WD | 294 | 86 | 154 |
| Honda CR-V Sport FWD | 423 | 260 | 73 |
| Toyota Tacoma TRD Off Road 4WD | 117 | 173 | 30 |
| Tesla Model Y Long Range (used - 2021) | 19 | 15 | 57 |
| Jeep Grand Cherokee Limited 4WD | 225 | 81 | 125 |
| Toyota Highlander XLE FWD | 207 | 235 | 40 |
| Toyota Corolla LE | 103 | 191 | 24 |
| Chevrolet Equinox LS | 53 | 102 | 23 |
| Ford Explorer XLT | 616 | 114 | 243 |
| Tesla Model 3 RWD (used - 2021) | 24 | 20 | 54 |
| Nissan Rogue SV | 678 | 445 | 69 |
| Jeep Wrangler Unlimited | 114 | 54 | 95 |
| Hyundai Tucson SEL | 253 | 320 | 36 |
| Subaru Crosstrek Limited | 15 | 79 | 9 |
| Honda Accord EX | 279 | 188 | 67 |
| Make/Model | Total For Sale | # Sold - 45 Days | Days Supply |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ford F-150 XLT Hybrid | 1378 | 352 | 176 |
| Chevrolet Silverado LT 4WD | 894 | 263 | 153 |
| Ram 1500 Big Horn/Lone Star | 1021 | 139 | 331 |
| Toyota RAV4 XLE Premium | 192 | 223 | 39 |
| Toyota Camry LE FWD | 139 | 151 | 41 |
| GMC Sierra Elevation 4WD | 331 | 63 | 236 |
| Honda CR-V Sport FWD | 352 | 322 | 49 |
| Toyota Tacoma TRD Off Road 4WD | 139 | 216 | 29 |
| Tesla Model Y Long Range (used - 2021) | 27 | 11 | 110 |
| Jeep Grand Cherokee Limited 4WD | 180 | 56 | 145 |
| Toyota Highlander XLE FWD | 250 | 250 | 45 |
| Toyota Corolla LE | 98 | 150 | 29 |
| Chevrolet Equinox LS | 25 | 87 | 13 |
| Ford Explorer XLT | 538 | 147 | 165 |
| Tesla Model 3 RWD (used - 2021) | 23 | 13 | 80 |
| Nissan Rogue SV | 601 | 399 | 68 |
| Jeep Wrangler Unlimited | 48 | 41 | 53 |
| Hyundai Tucson SEL | 194 | 366 | 24 |
| Subaru Crosstrek Limited | 5 | 60 | 4 |
| Honda Accord EX | 201 | 187 | 48 |
The trend couldn’t be more clear: there’s a massive oversupply of trucks, and a shortage of popular, more affordable crossovers, SUVs and sedans. Buyers are holding back on truck purchases, yet automakers keep producing more and more. They make less profit per affordable vehicle sold, and in these greedy times, they’re producing less and less of them. We saw it just the other day with the cancellation of the Chevrolet Bolt to make way for $80,000+ electric trucks.
Let’s talk about what you should do to overcome these obstacles when buying in 2023. With a but of insider know-how, buyers still have the upper hand.
Here’s the latest new car inventory numbers (nationwide).

With the latest market update in mind, CarEdge co-founder and auto industry veteran Ray Shefska wanted to share these timely recommendations with car buyers.
“My advice for buyers can be summed up in one word, patience. With dealer floor plan costs rising and inventory levels growing, a consumer’s patience should be rewarded with lower prices either via direct discounts from the dealership or in combination with manufacturer customer incentives in the form of rebates. Depending on how we see sales play out for the month of May, lower than what they had hoped for, is my expectation. I would not be surprised to see manufacturers offer both customer rebates and subvented interest rates in May to spur slowing sales. Dealers hate aged new vehicle inventory and with trucks sitting for so long, many dealers will react the only way they know how, and that would be discounting trucks to move them.
PATIENCE is the word of the day.”
To find the best deals in the current market, car buyers need to be flexible in their choices. Buyers may need to be open to different makes and models to take advantage of the best deals. For example, a buyer in the market for a new Honda CR-V may want to test drive the new Nissan Rogue or even a Ford Explorer, two models with more inventory. If you’re shopping for a model that’s in short supply, now’s probably not the time to be picky about paint color, wheels or other nonessentials.
To make informed buying decisions, car buyers should conduct thorough research on the models they are interested in. With CarEdge Data, buyers can access valuable information on depreciation, resale value, and more. Armed with this knowledge, buyers can negotiate better deals and avoid being taken advantage of by car dealerships. Don’t make a hasty decision – take the time to do your research and make an informed choice.
See behind-the-scenes local market data with CarEdge Car Search.
If you’re in the market for a new car in 2023, it’s more important than ever to make informed buying decisions. With CarEdge Data, you can access proven data on depreciation, resale value, and more to ensure that you get the best deal possible. Don’t let car dealerships take advantage of you – empower yourself with CarEdge Data today.


Are you in the market for a new car? If so, it’s important to consider the depreciation rate of the vehicle you’re interested in. Depreciation in vehicles is inevitable, but some cars hold their value better than others. At CarEdge, we’ve analyzed millions of car listings and other automotive data points to provide you with proven data that you can rely on to make informed decisions. Let’s take a closer look at the cars, SUVs and trucks with the best resale value.

Volkswagen: 85.53% resale value after 5 years
Even though they finally had to re-retire the Beetle, Volkswagen scored in the top half of vehicle manufacturers for value retention after 3, 5, and 7 years. See Volkswagen depreciation by model year.
Subaru: 84.41% resale value after 5 years
The low-inventory king is known for reliable all-weather capability at an affordable price. The Forester (#4), Legacy (#20), Crosstrek (#30) and Outback (#36) are all in the top 50 models for resale value. Despite keeping low inventory on dealership lots, Subaru maintains a great reputation for resale value.
Honda: 83.60% resale value after 5 years
The Civic, Accord and redesigned CR-V were all best-sellers in 2022. It’s no coincidence that these same models are in the top resale value rankings. Honda cars and SUVs are known for their longevity, reliability and strong resale value. As Honda finally enters the EV segment later this year with the all-new Honda Prologue, we wonder if their electric vehicles will earn the same great reputation.
Mazda: 83.29% resale value after 5 years
Mazda’s resale values have improved, relative to their peers, and their rankings have climbed to the Top 5 range at all three time intervals. Mazda’s U.S. market share has been steadily rising for years. The Mazda 3, MX-5 Miata, and CX-5 all rank in the top 50 models for resale value.
Toyota: 83.09% resale value after 5 years
Toyota as a brand, does very well in maintaining its value, consistently ranking at the top of popular brands. The Toyota Tacoma, Highlander, 4Runner, Prius and Sequoia all have better-than-average resale value. Compare Toyota resale values here.
Check out this depreciation calculator

| Rank | Model | 3 Year Residual Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Subaru Forester | 96.40% |
| 2 | Chevrolet Silverado 3500HD | 96.28% |
| 3 | Ford F-450 Super Duty | 95.47% |
| 4 | GMC Sierra 3500HD | 95.44% |
| 5 | Mitsubishi Mirage | 95.26% |
| 6 | Honda Ridgeline | 94.22% |
| 7 | Subaru Crosstrek | 94.00% |
| 8 | Dodge Charger | 93.78% |
| 9 | GMC Sierra 1500 | 93.41% |
| 10 | Jeep Compass | 93.24% |
| 11 | Chevrolet Traverse | 93.23% |
| 12 | Chevrolet Spark | 93.00% |
| 13 | Dodge Durango | 92.51% |
| 14 | Subaru Legacy | 92.49% |
| 15 | Toyota Tacoma | 92.47% |
| 16 | Ford Explorer | 92.00% |
| 17 | Honda Accord | 92.00% |
| 18 | Chevrolet Silverado 2500HD | 91.97% |
| 19 | Ram 2500 | 91.78% |
| 20 | Nissan Altima | 91.62% |
Source: CarEdge Depreciation Data

| Rank | Model | 5 Year Residual Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nissan Frontier | 88.55% |
| 2 | Honda Accord | 88.00% |
| 3 | Toyota Tacoma | 87.58% |
| 4 | Subaru Forester | 87.09% |
| 5 | Ford F-250 Super Duty | 87.00% |
| 6 | Volkswagen Tiguan | 87.00% |
| 7 | Ford F-350 Super Duty | 86.95% |
| 8 | Ford F-150 | 86.75% |
| 9 | Mazda 3 | 86.13% |
| 10 | Honda Civic | 86.00% |
| 11 | Kia Rio | 86.00% |
| 12 | Honda Pilot | 85.95% |
| 13 | Mazda MX-5 Miata | 85.80% |
| 14 | Toyota Highlander | 85.77% |
| 15 | GMC Canyon | 85.33% |
| 16 | Nissan Versa | 85.03% |
| 17 | Toyota 4Runner | 85.00% |
| 18 | Toyota Prius | 85.00% |
| 19 | GMC Sierra 1500 | 84.80% |
| 20 | Subaru Legacy | 84.73% |
Source: CarEdge Depreciation Data
Compare depreciation between models, all in one spot.
Depreciation in the value of cars is an inevitable reality, and it can significantly affect a vehicle’s overall cost. Therefore, it’s crucial to consider resale value when buying a car. CarEdge data shows that brands like Volkswagen, Subaru, Honda, Mazda, and Toyota have the best resale value after five years, and they maintain their great reputation for reliability, longevity, and value retention. This information is helpful to make informed decisions while purchasing a vehicle.
Love the data? We do too. That’s why we’ve created CarEdge Data, where you will find behind-the-scenes insights to inform your car buying decisions. With CarEdge Data, you unlock valuable market data:
✅ Black Book valuations: Get insider trade-in values from dealer auctions
✅ CarEdge Suggested Offer: Know the fair market value of every car on the market
✅ Negotiability Score: Discover the likelihood of negotiating based on market data
✅ CarEdge Recommendation: Get actionable next steps to buy a car
✅ Days Supply in your region
Looking for 1:1 help with your deal? Learn more about how you can partner with a car buying pro with years of experience with CarEdge Coach.
We’re here to help!

When it comes to purchasing a new or used car, the state you’re in can make a significant difference in terms of taxes, fees, and available inventory. We’ll take a look at the best and worst states to buy a car in 2025, focusing on factors like sales tax, insurance costs, documentation fees, and overall car supply. Let’s dive in and see how your state stacks up.
First, let’s explore the states that offer the most advantages when it comes to car buying. States like Alaska, Montana, Oregon, Delaware, and New Hampshire stand out due to their lack of statewide sales tax, as well as generally low fees when buying and registering a car. South Dakota and Iowa are close behind.
Several other states have low state sales tax rates, but many have higher fees that keep them out of our top rankings: Alabama (2%), Colorado (2.9%), Hawaii (4%), Louisiana (4%), Missouri (4.23%), New Mexico (4%), New York (4%), North Carolina (3%), Oklahoma (3.25%), South Dakota (4%), and Virginia (4.15%). However, local taxes can drive costs higher, especially in big cities and affluent suburbs.
Dealerships charge a documentation fee, or “doc fee,” to cover the cost of preparing and filing a sales contract. Many states don’t regulate doc fees, and the amount varies from state to state. In many cases, state taxes and registration fees can outweigh the advantages of low doc fees.
These states have the lowest doc fees in 2025, and as a result, are better states to buy a car in: Minnesota ($75), Arkansas ($110), Oregon ($115), South Dakota ($115), Iowa ($135), Texas ($150), Washington ($150), Indiana ($150). California is also on the list with a very low average doc fee of $85, but the high sales tax and low supply of new cars keeps it far off of the list of best states to buy a car in.

Now, let’s take a look at the states you might want to avoid when purchasing a vehicle. Documentation fees can be particularly high in Florida, Alabama, Virginia, and North Carolina, with fees ranging from $485 to $995. Florida stands out as one of the worst states for new car purchases, with no cap on doc fees (averaging $995). When it comes to vehicle registration, a few states stand out with costly fees:
Alabama, North Carolina, Iowa, and Florida aren’t far behind with registration fees all averaging over $300.
It’s important to point out that taxes and fees are only part of the picture. The existing supply of new cars in each state is also critically important. Nationwide, there’s an 83-day supply of new cars as of late May 2025. However, some states have might tighter supply. These are the states with the lowest supply of new cars in 2025:
With doc fees, registration fees, sales tax, and new car inventory all taken into consideration, it’s safe to say that the worst states to buy a car are: Mississippi, Florida, California, and North Carolina.
However, Florida’s abundant used car market can make it a better choice for used car buyers, thanks to the state’s older population. On the other hand, flood cars are a much bigger risk in Florida’s used car market.
Ready to outsmart the dealerships? With CarEdge Negotiation Expert, we’ll negotiate your car price to lock in big savings. Looking for a DIY path to savings? Shop confidently with CarEdge Pro, our most affordable option for empowered car buying. Looking to lease? We can help with that too!
Learn more about CarEdge’s car buying help →


Dealer lot inventory is on the rise, but where are the deals at?! As we move further into 2023, many potential car buyers are wondering, “is now a good time to buy a car?” and “will car prices go down in 2023?” The good news is that recent market trends indicate that the tide is starting to turn, with car prices slowly beginning to decrease and negotiability on the rise. However, there are big differences between the new and used car markets today. Let’s take a closer look at the details.
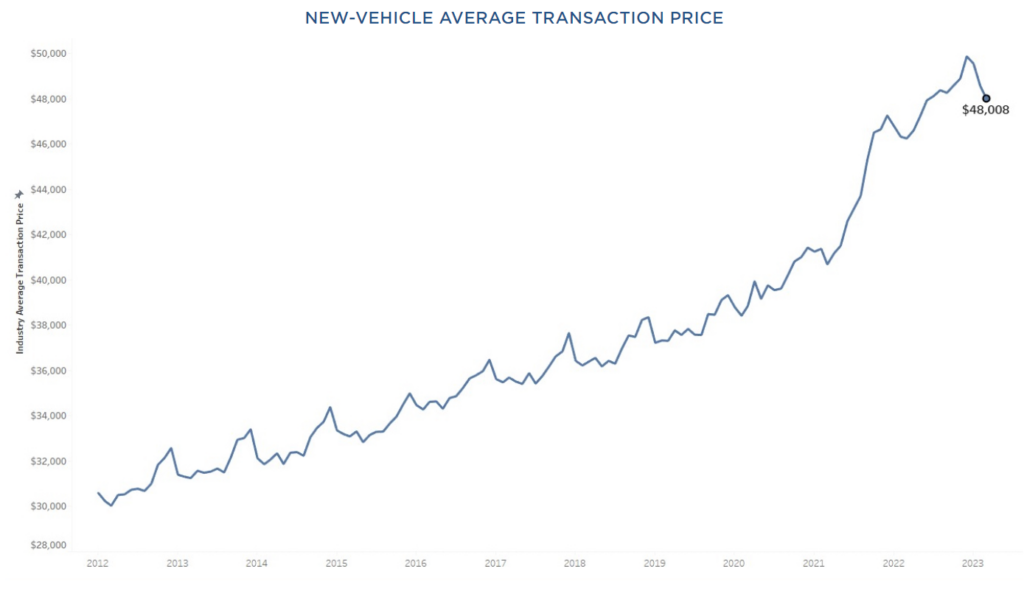
According to CarEdge’s Ray Shefska, recent trends suggest that there’s good news for car buyers, with prices gradually decreasing and more room for negotiation on the horizon.
Ray notes that “March broke a string of 20 straight months where the average new car prices transacted at above MSRP, in March the average price paid was $171 below MSRP.”
“Although this drop might not seem significant, it’s a noteworthy development, indicating that dealerships are becoming more open to selling cars at lower prices,” he explained. Car manufacturers are increasing incentives to attract more buyers to the market, ultimately benefiting car shoppers.
CarEdge’s Car Coaches note that patience will be rewarded as we head into the summer 2023 car buying season. “Consumers who are patient will find themselves in a much better position as negotiability should increase as we get into the summer months.”
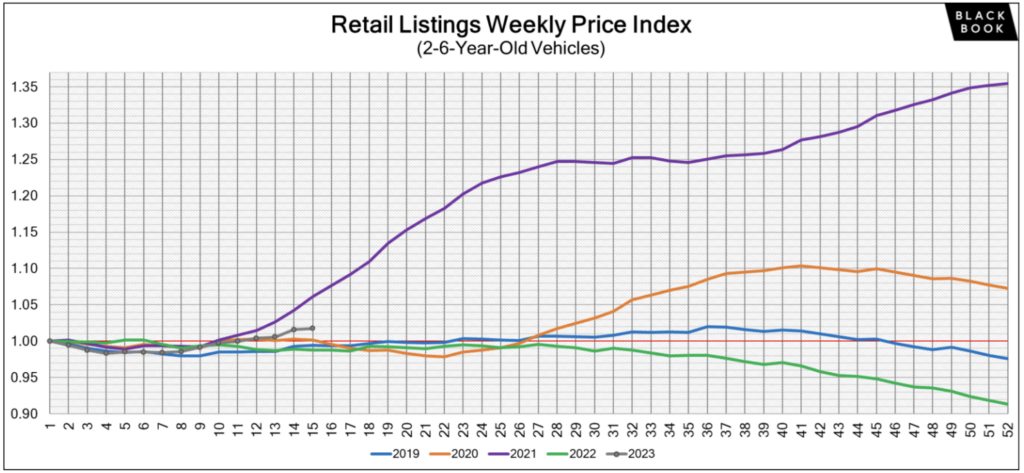
It’s important to note that there are considerable differences between the new and used car markets. New car transaction prices are steadily dropping as dealers try to move more inventory after years of nearly vacant lots. On the other hand, used car prices are increasing as of spring 2023. The latest used car price data from Black Book shows that after 30 weeks of wholesale price declines, used car prices have actually increased for the past several weeks. In April, used car prices increased at the retail level too.
CarEdge’s Car Coaches don’t expect rising used car prices to become a new long-term trend like we saw in 2021 and early 2022. However, there could be a month or two of additional slight price hikes.
We track used car prices weekly here.
How do rising interest rates affect car buying? Of course, buyers who finance are going to pay more in interest, no matter their credit score. But other things change too. Despite higher APRs, there can be benefits for buyers. Car dealers pay interest on lot inventory until it is sold. Think of dealer floor plan financing almost like a credit card made solely for purchasing vehicle inventory. When the federal reserve raises the cost of borrowing money, all kinds of credit will become more expensive, and that includes car lot floor-planning.
With higher floor plan costs, rising lot inventories and incentive spending on the rise, dealers will be motivated to negotiate. Therefore, the longer you can wait to buy a car in 2023, the more likely you’ll be able to negotiate thousands off of your deal.
See the best manufacturer incentives this month (updated)
Furthermore, Ray predicts that it will be a lot easier to secure a deal below MSRP as we get deeper into summer. In fact, the latest data from Kelly Blue Book shows that for the first time in two years, new-vehicle transaction prices fell below MSRP in March. The CarEdge Coaches expect that trend to continue.
Sadly, you and I are well aware that cars are far from cheap these days. The average price paid for a new car is still around $48,000. If you’re looking to go electric, expect to pay 20% more. Even in this market, our Coaches have proven even the toughest new and used cars are negotiable. Check out these success stories from happy drivers around the nation. CarEdge Coaches have even negotiated thousands of dollars off of EV prices in 2023.

We’re real people empowering you to save real money on your next auto. How can we help? Check out hundreds of 100% free resources, great YouTube videos, and the fastest-growing online auto forum today, the CarEdge Community. We just launched Dealer Reviews, where you can see nearly 3,000 crowdsourced car dealer and deal reviews.
Looking for behind-the-scenes auto market data to inform your buying decisions? That’s exactly why we created CarEdge Data. Unlock the Black Book car valuations that dealers use, CarEdge negotiation scores, official recommendations, and local market data for every car on CarEdge Car Search with CarEdge Data.
Ready for expert 1:1 help with your deal? Our Car Coaches are ready to work with you to secure the best deal on out-the-door prices, financing, and more. Learn more about our CarEdge Coach unlimited access plan. We look forward to meeting you.