CarEdge saved me over 4,500 dollars on a brand new Honda Pilot. I can't say thank you enough.
Price intelligence
Find a wide range of vehicle listings with market insights on new and used listings near you.

Help us personalize your CarEdge experience — it only takes a second.
Your answers help us personalize your CarEdge journey — we’ll follow up with tips and next steps that match your buying timeline.


Update: Every day that we wake up to higher gas prices, the case gets stronger for EV adoption. If only EV prices weren’t sky-high. With gas at $4.50, the average American driver commuting 15,000 miles per year can easily save $150 per month or more by going electric. Check out the details below.
Charging an electric vehicle is a whole new experience, one that brings advantages and disadvantages for drivers. If you’ve been stopping at gas stations for decades, the thought of plugging in and waiting for your car to charge may be a bit too much to swallow. But over 80% of EV charging is done at home, where the cost savings are greatest. Two out of three American drivers are considering going electric for their next vehicle, and billions of dollars are being funneled into EV development and infrastructure.
EVs have a higher upfront cost than combustion vehicles, so it’s important to find ways of making up for the expense with fuel savings. Unfortunately, not all charging options are affordable. Here’s how you can save money when charging your EV in 2022.

When do you usually charge your phone? While you sleep at home? Oddly enough, for most drivers, that’s exactly how their EVs are charged! Data from the US Department of Energy shows that the vast majority of electric vehicle charging is done at home. Whether you plug in to a simple 120 volt outlet in your driveway or have a more powerful 240 volt outlet in your garage, charging at home is usually the most affordable way to power up.
In the US, the average residential electricity rate is $0.14 per kilowatt-hour, however rates vary widely from one state to another. In Hawaii, the average rate is a whopping $0.34 per kWh, while it’s between $0.10 and $0.14 per kWh in more affordable energy states like Washington and Texas.
What does that all mean? Say you have a level 2 charger capable of filling up your battery from empty in about 7 hours. Plug in every evening, and wake up with a full battery every morning. What did that full ‘tank’ of electrons cost? Let’s consider a real-world example. The 2022 Tesla Model 3 has a 82 kWh battery, so at average American residential rates, at home charging a Tesla Model 3 at home costs just $11.48 for a full charge. That’s enough electrons for 358 miles of driving.
What about if the same Model 3 owner lived in California instead? At typical California residential electricity rates, the same charge would cost $18.04. Considering that a tank of gas costs over $75 today, the savings add up. But clearly, it depends on the rates you pay for power and miles driven per year to maximize savings. If you’d like to know more about average residential electricity rates in each state, you can find that information here.
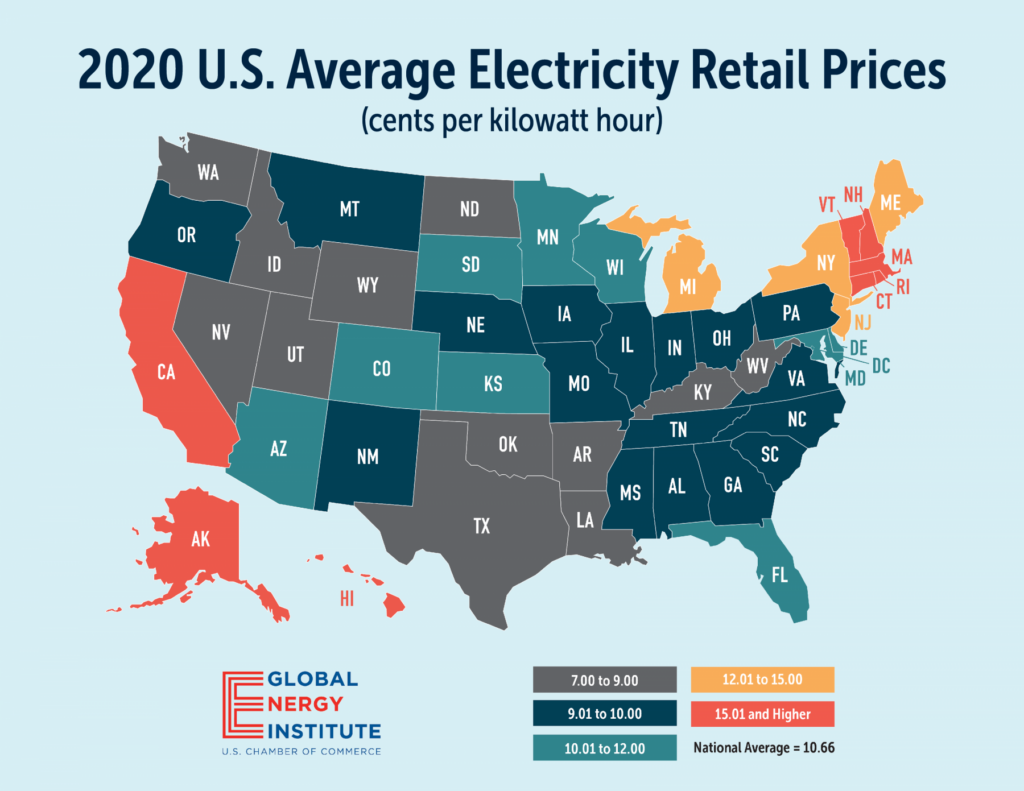
Here’s how much EV drivers from each state can expect to pay for a full charge. The examples below specifically reflect an EV with an 82 kWh battery, such as a Tesla Model 3 or Model Y. My own Hyundai IONIQ 5 has a 72.5 kWh battery.
The stark difference between home charging and public fast charging highlights the fact that going electric likely only brings savings when most charging is done at home.
| State | Residential Electricity Rate ($ per kWh) | Cost of Charging to 100% at Home (82 kWh battery) | EV Fuel Savings Compared to Filling an 18 Gallon Tank at $4.50/Gal | Annual Savings: 15,000 miles/year, 25 MPG versus 300 miles on a charge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alabama | $0.14 | $11.48 | $69.52 | $2,126 |
| Alaska | $0.23 | $18.86 | $62.14 | $1,757 |
| Arizona | $0.13 | $10.66 | $70.34 | $2,167 |
| Arkansas | $0.11 | $9.02 | $71.98 | $2,249 |
| California | $0.22 | $18.04 | $62.96 | $1,798 |
| Colorado | $0.14 | $11.48 | $69.52 | $2,126 |
| Connecticut | $0.23 | $18.86 | $62.14 | $1,757 |
| Delaware | $0.14 | $11.48 | $69.52 | $2,126 |
| DC | $0.14 | $11.48 | $69.52 | $2,126 |
| Florida | $0.12 | $9.84 | $71.16 | $2,208 |
| Georgia | $0.13 | $10.66 | $70.34 | $2,167 |
| Hawaii | $0.34 | $27.88 | $53.12 | $1,306 |
| Idaho | $0.11 | $9.02 | $71.98 | $2,249 |
| Illinois | $0.14 | $11.48 | $69.52 | $2,126 |
| Indiana | $0.14 | $11.48 | $69.52 | $2,126 |
| Iowa | $0.13 | $10.66 | $70.34 | $2,167 |
| Kansas | $0.13 | $10.66 | $70.34 | $2,167 |
| Kentucky | $0.12 | $9.84 | $71.16 | $2,208 |
| Louisiana | $0.12 | $9.84 | $71.16 | $2,208 |
| Maine | $0.18 | $14.76 | $66.24 | $1,962 |
| Maryland | $0.14 | $11.48 | $69.52 | $2,126 |
| Massachusetts | $0.23 | $18.86 | $62.14 | $1,757 |
| Michigan | $0.18 | $14.76 | $66.24 | $1,962 |
| Minnesota | $0.14 | $11.48 | $69.52 | $2,126 |
| Mississippi | $0.12 | $9.84 | $71.16 | $2,208 |
| Missouri | $0.11 | $9.02 | $71.98 | $2,249 |
| Montana | $0.12 | $9.84 | $71.16 | $2,208 |
| Nebraska | $0.11 | $9.02 | $71.98 | $2,249 |
| Nevada | $0.13 | $10.66 | $70.34 | $2,167 |
| New Hampshire | $0.21 | $17.22 | $63.78 | $1,839 |
| New Jersey | $0.16 | $13.12 | $67.88 | $2,044 |
| New Mexico | $0.14 | $11.48 | $69.52 | $2,126 |
| New York | $0.21 | $17.22 | $63.78 | $1,839 |
| North Carolina | $0.12 | $9.84 | $71.16 | $2,208 |
| North Dakota | $0.12 | $9.84 | $71.16 | $2,208 |
| Ohio | $0.13 | $10.66 | $70.34 | $2,167 |
| Oklahoma | $0.13 | $10.66 | $70.34 | $2,167 |
| Oregon | $0.12 | $9.84 | $71.16 | $2,208 |
| Pennsylvania | $0.15 | $12.30 | $68.70 | $2,085 |
| Rhode Island | $0.22 | $18.04 | $62.96 | $1,798 |
| South Carolina | $0.14 | $11.48 | $69.52 | $2,126 |
| South Dakota | $0.13 | $10.66 | $70.34 | $2,167 |
| Tennessee | $0.12 | $9.84 | $71.16 | $2,208 |
| Texas | $0.13 | $10.66 | $70.34 | $2,167 |
| Utah | $0.11 | $9.02 | $71.98 | $2,249 |
| Vermont | $0.21 | $17.22 | $63.78 | $1,839 |
| Virginia | $0.13 | $10.66 | $70.34 | $2,167 |
| Washington | $0.11 | $9.02 | $71.98 | $2,249 |
| West Virginia | $0.14 | $11.48 | $69.52 | $2,126 |
| Wisconsin | $0.15 | $12.30 | $68.70 | $2,085 |
| Wyoming | $0.12 | $9.84 | $71.16 | $2,208 |

If you already have a 240 volt dryer outlet within reach, you’re all set for just about any scenario. If you don’t, you’re left with two options. If you drive less than 40 miles on most days and live within a reasonable distance of a public charger (in case you need it), you will save the most money by using the so-called ‘trickle charge’ supplied by the charger included with the car. You simply plug into a standard three-prong 120 volt wall outlet. This is called level 1 charging.
Depending on the vehicle, trickle charging typically adds 3-4 miles of charge per hour to the battery, or about 40 miles per night if you leave your car plugged in. So, how much does it cost to charge an electric car? If the above scenario describes your driving habits, you’ll just pay the same residential electricity rates that your pay to power your home.
If that’s not quite enough recharge for your daily needs, you’ll either need to make weekly visits to public fast chargers, or spend anywhere from $800 – $2000 on installation of a level 2 charger. Level 2 chargers supply more power in less time. They plug into a 240 volt outlet, the exact same kind that is used for dryers, ovens and other large appliances at home.
If you already have a conveniently located dryer outlet within reach of where you park the car, you can purchase a power splitter for as little as $300. Splitters send charge to the home appliance (such as a dryer) when needed, and then divert power to charging the car when the appliance is not in use. This saves A LOT of money versus getting electrical work done!
In summary, if you drive less than 40 miles a day, it usually makes the most sense to avoid the costly level 2 charger and stick with a regular wall outlet. If you drive significantly more, consider installing a level 2 charger or simply topping off your battery once or twice a week at a local public fast charger to avoid the expense of electrical work.

First, there’s one thing we need to make clear. Electric vehicles are not meant to be charged at public DC (direct current) fast chargers every time a charge is needed. It stresses the battery, and it costs a lot more than charging at home. For instance, fast chargers can charge a Model 3 from 10-80% in less than 20 minutes. That much energy transfer puts wear on the vehicle’s battery management system. Fast charging is great for road trips or when you’re in a pinch, but that’s all they’re meant for.
How much can you expect to pay for charging at a public DC fast charging station? Let’s consider the two largest charging networks in the nation: Tesla Superchargers and Electrify America.
As of early 2022, most Tesla Superchargers charge $0.28 per kWh of electricity. For a 2022 Tesla Model Y with a 82 kWh battery pack, that adds up to a cost of $22.96 to go 330 miles on a charge. Some Superchargers have variable pricing dependent on demand charges, as noted on Tesla’s Supercharging support page. “Certain Supercharger stations offer on-peak and off-peak rates. The rates and peak times are both displayed in the navigation application on the touchscreen.”
Depending on state and local regulations, some Tesla Superchargers charge per minute, rather than per kilowatt-hour of electricity. Tesla recently updated the rate structure for their per-minute Superchargers. With Tesla’s plug-and-charge, customers simply plug in the vehicle and the charger communicates with the car, begins charging and bills the customer’s Tesla account.
Here’s how the updated rate structure is tiered in 2022:
Source: Tesla

Over at Electrify America, customers can either pay $0.43 per kWh of electricity, or become a Pass+ member for just $4/month and charge at $0.31 per kWh. Having such an affordable membership plan is an interesting approach. That is to say, it almost seems like Electrify America is aiming to become a subscription that everyone with an EV will buy into for a sense of range security, even if they rarely use the network. Down the road, I’m sure prices will go up.
For a Ford Mustang Mach-E, filling up the 98 kWh battery from empty will cost $30.38 with the Pass+ membership. However, the cost jumps to $42.14 without it. Clearly, the fuel savings we often associate with going electric evaporate if charging costs are too high.
| Cost of Charging to 100% at a Tesla Supercharger | Cost of Charging to 100% at Electrify America as a Member | Cost of Charging to 100% at Electrify America as a Guest | Cost of Filling up an 18 Gallon Tank of Gas at $3.25/Gallon |
| $22.96 | $25.42 | $35.26 | $58.50 |

If you know someone who pulls up to Tesla Superchargers in their 2014 Model S and leaves without paying a dime, don’t expect the same perks when shopping for a 2022 Tesla. Early adopters received free supercharging ‘for life’, and there are plenty of Tesla owners out there who keep driving their high-mileage, slow-charging old Model S just for the free charging incentive.
If you’re hoping to score free charging with any of the 2022 EV models, I’ve got good news for you. Many 2022 models come with free charging at Electrify America charging stations. These new EVs all come with a free charging incentive for a limited time:
Some employers, especially large corporations and tech companies, offer free charging for EVs at dedicated parking spots. However, if your employer doesn’t offer charging, maybe you can be the one to spark the idea and help make it happen.
Prices have plummeted in recent years, and having an EV is yet another incentive to go solar. Most utility customers can participate in a net metering program that compensates homeowners for unused solar electricity contributed to the grid. If the sun is shining bright while you’re away at work, you still receive bill credits for the unused power your panels generated. The utility bill credits you’ll receive may cover the entire cost of charging your car. That’s 100% clean, free power for both your home and transportation!
How much does it cost to charge an electric car? As you can see, it depends on utility rates, incentives and if you charge at home or at public fast chargers. Fuel savings is one of the greatest benefits of switching from a combustion vehicle to an electric vehicle. As your consumer advocate, we want to make it clear that EVs don’t always save money. However, for the vast majority of American drivers, affordable electricity rates mean that at least $1,000 could be saved each year by going electric. And that doesn’t include the lower maintenance costs that most EVs have. For those who are fortunate to have a place to plug in at home or work, switching to an electric vehicle is a no-brainer.
Have any questions or comments? How are you feeling about the electrification of the auto industry? Let us know in the comments below, or check out the CarEdge Community forum at caredge.kinsta.cloud. You can also reach out to me at [email protected].


(Updated for Summer 2022)
As anyone who’s fallen head over heels for one of the many 2022 electric vehicles and clicked that ‘Order’ button can attest, just because you can order an EV in 2022 doesn’t mean you can drive it home this year. This was a problem I faced myself, but I finally broke the code and got a Hyundai IONIQ 5 at MSRP (here’s how).
Soon after I began my online car search, it became clear that if I wanted a brand-new vehicle, my options were limited by availability. To make the most of the situation, I thought I’d share what I’ve learned about the availability and estimated delivery times for EVs on the market today. Here’s what we know as we kick off the new year.
Note: These are fully-electric models that can either be ordered now or purchased at a dealership today. Many more have been announced but are not yet officially available.
| Make | Model | Class | Starting MSRP | Estimated Delivery/Lot Availability* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Audi | e-tron | crossover SUV | $65,900 | Available Now |
| Audi | Q4 e-tron | crossover SUV | $43,900 | Available Now |
| Audi | RS e-tron GT | sedan | $103,445 | Available Now |
| BMW | iX | SUV | $88,050 | Mid-2022 |
| BMW | i4 | sedan | $55,400 | Mid-2022 |
| Cadillac | Lyriq | SUV | $62,990 | Late-2022 |
| Chevrolet | Bolt | hatchback | $31,000 | Available Now |
| Chevrolet | Bolt EUV | crossover SUV | $33,500 | Available Now |
| Fisker | Ocean | crossover SUV | $37,499 | 2023 |
| Ford | Mustang Mach-E | crossover SUV | $43,895 | Available Now |
| Ford | F-150 Lightning | truck | $39,974 | 2023-2024 |
| GMC | Hummer EV | truck | $99,995 | Mid-to-late 2022 |
| Hyundai | IONIQ | crossover SUV | $33,245 | Available Now (Discontinued) |
| Hyundai | IONIQ 5 | crossover SUV | $43,650 | Available Now |
| Hyundai | Kona | crossover SUV | $34,000 | Available Now |
| Jaguar | I-Pace | crossover SUV | $69,900 | Available Now |
| Kia | Niro | crossover SUV | $39,990 | Available Now |
| Kia | EV6 | crossover SUV | $42,115 | Available Now |
| Lucid | Air | sedan | $77,400 | Mid-2022 |
| Mazda | MX-30 | crossover SUV | $33,470 | 2022 - CA Only |
| Mercedes | EQS | sedan | $102,310 | Available Now |
| Mercedes | EQB | SUV | ~$55,000 | Late 2022 |
| Nissan | Leaf | hatchback | $27,400 | Available Now |
| Nissan | Ariya | crossover SUV | $47,125 | Late 2022 |
| Polestar | Polestar 2 | sedan | $45,900 | Available Now |
| Porsche | Taycan | sedan | $82,700 | Available Now |
| Rivian | R1T | truck | $67,500 | 2023 |
| Rivian | R1S | SUV | $70,000 | 2023 |
| Subaru | Solterra | crossover SUV | $46,220 | Mid-to-late 2022 |
| Tesla | Model S | sedan | $94,990 | Late 2022 - 2023 |
| Tesla | Model 3 | sedan | $46,990 | Mid-to-late 2022 |
| Tesla | Model X | SUV | $104,990 | 2023 |
| Tesla | Model Y | crossover SUV | $62,990 | Late 2022 - 2023 |
| Toyota | bZ4X | crossover SUV | $43,215 | Mid-to-late 2022 |
| Volkswagen | ID.4 | crossover SUV | $40,760 | Mid-2022 |
| Volvo | XC40 Recharge | crossover SUV | $55,300 | Available Now |
| *For a vehicle ordered in May 2022, unless there's existing dealership supply. |
A few things might stand out to you on this list. Not a lot of options are available if you need a new vehicle right now. VW Group’s new EVs are available at many dealerships, although there are reports of major dealer markups. It’s quite easy to find EVs of the previous generation on dealer lots. Think Kia eNiro, Hyundai Kona EV, Nissan Leaf and the like.
The vast majority of 2022 electric vehicles are crossovers. No surprise there given the sales trends over the past decade. Honda doesn’t have a single EV arriving in the North American market until the 2024 Prologue electric SUV. That is surprising considering the popularity and good reputation of the brand. What will it take for automakers to catch up to demand? An end to the chip shortage would be a great step in the right direction. There’s also the supply versus demand factor. Ford, Rivian, Tesla and VW are all swamped with orders well into 2022, and even into 2023. All except Tesla are EV newcomers who are facing the same production ramp-up struggles that Tesla just barely survived a few years ago. We’ll update this page regularly as more information becomes available, so save it to your bookmarks!
Did we miss anything? Let us know in the comments below, or shoot an email to [email protected].