CarEdge saved me over 4,500 dollars on a brand new Honda Pilot. I can't say thank you enough.
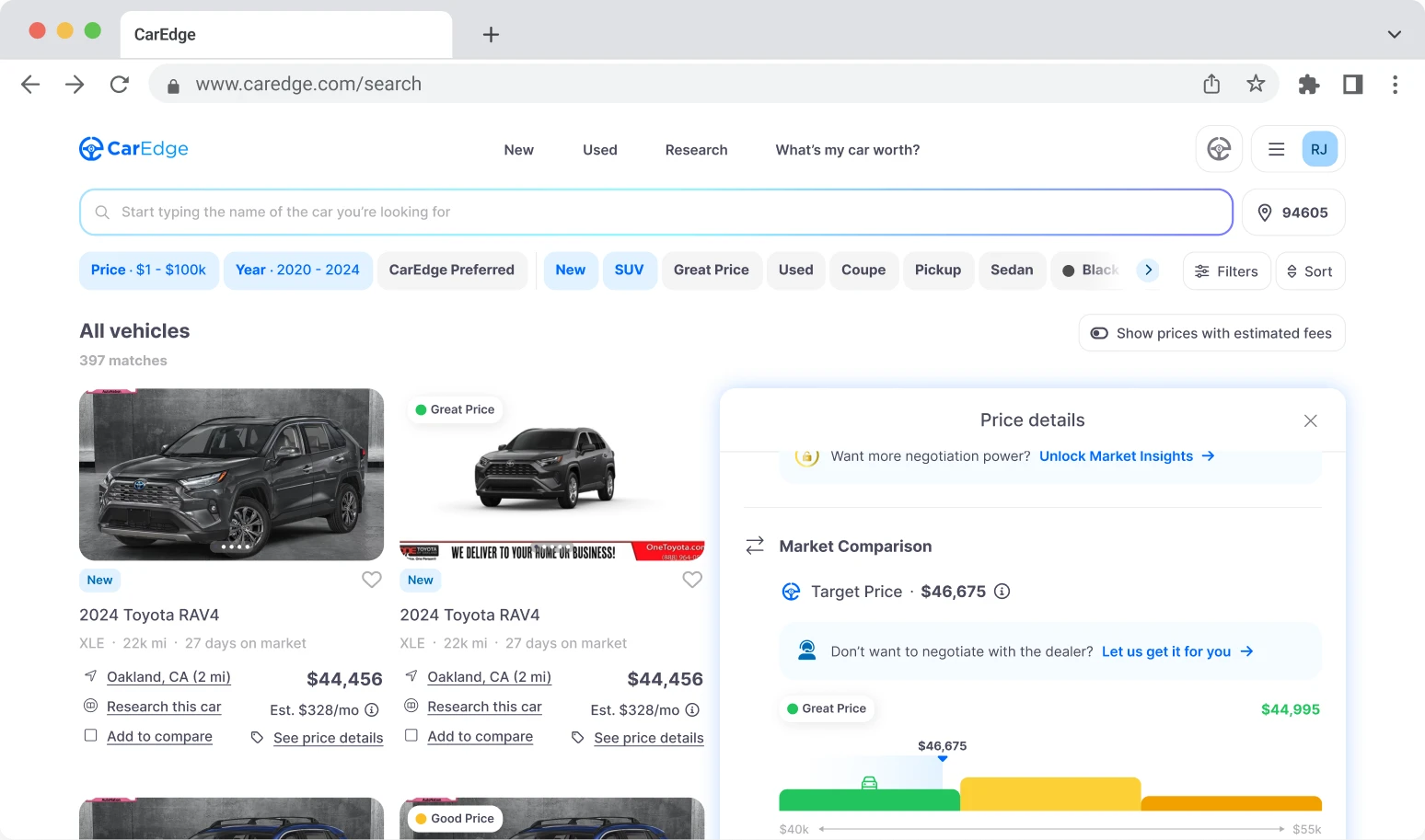
Price intelligence
Find a wide range of vehicle listings with market insights on new and used listings near you.

Help us personalize your CarEdge experience — it only takes a second.
Your answers help us personalize your CarEdge journey — we’ll follow up with tips and next steps that match your buying timeline.
Used car buying can be stressful. Our Honda Certified Pre-Owned review is meant to help.
One of the perks of buying a certified pre-owned vehicle is knowing that it meets the manufacturer’s standards for quality and worthiness. That being said, every manufacturer has a slightly different certified pre-owned program, and Honda actually offers two variants.
HondaTrue Certified, and HondaTrue Certified+ are two levels of certified pre-owned offered by Honda on their vehicles. Below we’ll tell you what you need to know about both before you buy your next Accord, Civic, Odyssey, or CRV.
CarEdge score: 7/10
HondaTrue Certified+ is Honda’s premier CPO program. Vehicles that are less than one year old qualify for Certified+ distinction.
CarEdge score: 6/10
Honda’s “non-plus” variant of certified pre-owned is valuable for customers. Below we breakdown what we like and dislike about both CPO programs.
What’s to love about Honda’s CPO program?
What’s missing or lacking about the program?
If you’re interested in reading all the fine print, you can click here to access the entire CPO warranty booklet. Below we’ll go in depth into key aspects of the certified pre-owned program.
Expendable Parts
Maintenance procedures
Clutch, Brakes & Tires
Batteries & Bulbs
This limited warranty does not cover any emission-related repairs, including but not limited to the following:
This limited warranty does not cover any item concerning the vehicle’s general appearance including cleaning, polishing, normal wear and deterioration of any part.
Body Parts & Trim
Interior Parts, Upholstery & Trim
Glass & Mirrors
Wheels
As you can see, a lot of items are not covered by the CPO warranty. This is one of our biggest frustrations with Honda’s certified pre-owned program. Unfortunately for the customer, they will likely end up having to pay out of pocket for something on their CPO vehicle, even though they are paying for the privilege of it coming with this extra warranty.
Similar to Toyota’s certified pre-owned program, Honda also offers a 12 month roadside assistance program for CPO vehicles. This is a nice perk, and one that more and more manufacturers are offering.
The specific benefits that come from Roadside Assistance are:
For a vehicle to qualify for CPO status, it must pass a rigorous 182-point inspection by a Honda certified technician. The inspection includes confirming that no aftermarket parts have been added to the vehicle, that the entire interior, exterior, and underside of the vehicle are of high quality, and that the tires, brakes, and engine are in good working condition.
For a complete list of what is included in the inspection, you can click here.
We hope you found this Honda Certified Pre-Owned review helpful. Navigating the car buying journey can be challenging, and we’re here to help!
When it comes to buying a used car, the process can be intimidating. One way to make it “easier” is to buy a certified pre-owned car. Toyota offers a certified used program, and below we’ll discuss its pros and cons. If you’re thinking about buying a certified pre-owned RAV4, Highlander, Camry, or Corolla, you’ll want to read this brief guide before you sign on the dotted line. Here is CarEdge’s Toyota certified pre-owned review.
CarEdge score: 7/10
We rate Toyota’s certified-pre owned program a 7 out of 10. There is a lot to like about Toyota’s used car certification, and a few things to be left longing for.
What’s to love about Toyota’s CPO program?
A complete breakdown of Toyota’s certified pre-owned program can be found here: https://www.toyotacertified.com, and I strongly recommend you become familiar with that website if you are considering purchasing a Camry, Corolla, RAV4, etc, etc. Below we breakdown the key features of each primary component of the CPO program.
If you’re thinking about buying a car, you might enjoy this article if you haven’t read it already: How Much Do Dealers Markup Used Cars?
Certified pre-owned Toyotas come with two warranties; a comprehensive bumper-to-bumper warranty, and a powertrain warranty. As with all warranties, there are a few disclaimers that you need to be familiar with. For example, on the 12-month/12,000-mile comprehensive warranty there is a laundry list of items that are not covered.
All interior and exterior cloth, leather, and stitching including convertible tops and/or vinyl tops including but not limited to: any vibration, deterioration, discoloration, disfigurement, warping, fading, staining, stretching, ripping, punctures, tearing, and/or scratches.
What does this mean for you? If something breaks in your certified pre-owned Toyota vehicle, the odds are it might not be covered by your one year warranty. On the plus, the powertrain warranty is much more comprehensive, and Toyota stands by that warranty for 7-years or 100,000 miles (from the date of first purchase), whichever occurs first.
All certified used Toyota vehicles come with one year of roadside assistance. This is a nice perk and covers a variety of “oh no” moments like:
To become a certified used Toyota, a vehicle must pass a rigorous 160 point inspection (165 for fuel cell vehicles, and 174 for Hybrids). One thing we love about the Toyota certified pre-owned inspection is that it covers both mechanical and cosmetic aspects of the vehicle, and it must be completed by a factory trained technician.
The complete list of what is inspected can be found here: https://www.toyotacertified.com/160-point-inspection
Overall, our review of the Toyota certified pre-owned program is positive. We wish there were more items covered by the comprehensive warranty, and that the warranty lasted longer. We appreciate the powertrain warranty, 160 point inspection, and roadside assistance programs.
If you’re in the market for a Toyota vehicle and you’re torn between new, used, or certified pre-owned, you wouldn’t be making a mistake to consider a CPO vehicle.

Have you ever wondered how car dealerships actually make money? You’re not alone. Many car buyers worry they’ll get taken advantage of. No one wants to be the customer who unknowingly hands a dealer thousands in profit.
👉 The truth is, dealerships make money in three main ways: vehicle sales, service and parts, and the Finance & Insurance (F&I) department.
Whether you’re shopping for a car, curious about the business side of dealerships, or just stumbled across this post, you’re in the right place. After spending 43 years in the car business, I’ve seen it all—and I’m here to break down exactly how dealers turn a profit.
Let’s take a closer look at where the money really comes from.

It seems counter-intuitive to suggest that car dealerships don’t make money selling cars. Why be in the car business if you don’t make money from selling cars?
This is a valid question, and unless you really understand how car dealerships operate, its answer is shrouded in secrecy. The reality is, most car dealerships don’t make much profit from selling cars. Some do (and we’ll discuss how), but for most, car sales don’t make up the majority of profit generated at a dealership. Let’s explore why.
Regardless of selling a new car or a used car, there are two separate parts of a car deal where the dealer can make money. They are referred to as the “front-end” and the “back-end” of the deal.
The front-end of the deal is everything that happens when you are working with the salesperson. The back-end of the deal is everything that happens after the salesperson is out of the picture, and the Finance Manager steps into the picture.
In theory, you can have a used car sale with no frontend profit and a lot of backend profit. Or you could have a new car deal with a lot of frontend profit and no backend profit. Or, vice versa.
If you hear a dealer say, “we are taking a huge loss on the front-end, you better make up for it on the back-end of the deal,” you know that means they aren’t making much (or any) money on the sale of the car. Their goal is now to make money in the F&I part of the sale.
First, we’re going to focus on front-end profit. Back-end profit is covered below in the F&I section. As you’re about to learn, selling cars is simply a means to sell other things.
The manufacturer’s suggested retail price (MSRP) of a car, as well as any applicable charges and fees (i.e. destination charges) are listed on every new vehicle’s Monroney sticker. The Monroney sticker provides you with a line-by-line overview of what is included on every new car sold in the United States. You may also see an addendum placed on the car if the dealer has added additional accessories or charges. Luckily, we made it possible to see the window sticker for any car by VIN.
The price you see on the window sticker has some built in profit for the dealer. Why then am I suggesting that dealers don’t really make money from selling new and used cars? It’s because most dealers don’t sell their cars at its list price. Most car deals are negotiated to a lower sale price.
As a general rule of thumb, the mark up on a new car can range from as little as 2 or 3% for your economy brands (Kia, Hyundai, etc.), to more than 10% for luxury vehicles (Mercedes-Benz, BMW, etc.). Trucks are also known as high-margin sellers. The more luxurious and expensive the car, the more margin built into the MSRP price.
That means if you’re looking to buy a new Kia, and the total price listed on the window sticker is $18,000, there may only be $360 in profit built into the sale of that car. However, on the other end of the spectrum, a $150,000 Mercedes-Benz could have upwards of $15,000+ profit built into its list price.
Used cars follow this pattern as well. The cheaper the car, the less margin built into its list price. The more expensive the car, the more potential for markup. With used cars, dealers have to base their pricing on what the market is willing to pay.
On average, there is typically somewhere between $1,500 and $3,000 of margin built into used cars prices.
So do dealers make a killing selling new and used cars? 99% of the time the answer is no. Do some people overpay for a car, and the dealer makes a lot of front-end profit? Yes, but it doesn’t happen often.
During my career, I sold cars where we lost thousands of dollars on the front-end. Why did I let the customer get such a good deal? We did it in order to hit our monthly volume sales objectives from the manufacturer. Remember what I said before? Car dealerships are a lot like grocery stores, they depend on volume. That reality couldn’t be more true when dealers are incentivized to sell more cars with less profit built into each sale by the manufacturer.
Manufacturers also incentivize dealers to sell more cars by setting lofty monthly, quarterly, and annual sales volume goals. If these sales goals are attained (and surpassed), result in hundreds of thousands, if not millions of dollars for the dealership.
It is in attaining these monthly, quarterly, and annual sales objectives that car dealers can make money from selling cars.
Why do manufacturers wave millions of dollars in front of dealerships to get them to take losing deals to hit their volume objectives? As with all “goals” or incentive plans, there is a psychological answer and a practical answer.
Manufacturers, many of which are publicly traded companies that have shareholders to please, need to show growth. How do you show growth? You sell more cars. How do you sell more cars? You incentivize your dealer network to sell more cars by losing money on the sale of each car.
Why does this work? Because investors and shareholders are more excited by growth (selling more cars), than by profits (actually making money on each car sold). In my estimation, these practices won’t last forever. But, for now, that’s the way the car business works.
Many dealerships will take losses on deals (especially towards the end of a month) in order to hit their factory incentive threshold. If a dealership doesn’t hit their goal set from the factory, they risk not making any money that month.
In my career, I’ve seen manufacturer incentives that pay dealerships based on what percentage of goal they attain. For example, let’s say a dealership has a goal of selling 100 new cars in June. If they attain 95 percent to 105 percent of that goal (95 to 105 cars sold), the factory will pay them $1,000 per car sold. But, if the dealership is able to attain between 105 and 115 percent of their goal the factory will pay $1,250 per car. It can go up from there.
Even with all this money being thrown around, car sales still represent a small profit generator for the dealership. At the end of the day, car sales exist to facilitate the other revenue generating areas of the dealership: the F&I office (aka the back-end), and the Service department.
A growing area of importance for car dealerships is in the Finance and Insurance office. F&I, as it’s affectionately referred to, has always been an important revenue generator for car dealers, but now more than ever it’s becoming a major driver of profit.
If you’ve ever bought a car before, you’re very aware of the paperwork you need to sign before the car is officially yours. It’s a lot, and it can be quite intimidating. The process you went through was probably something like this:
Yea, I know, buying a car is a real pain.
Once you are “handed off” to the Finance Manager, you begin the second sales process. You thought that now that the salesperson was gone the sales process was over? No way!
Car dealerships make money in F&I in a few different ways.
It’s important to understand that if you finance your purchase through a dealership they will make money on the loan. Don’t get too upset about this.
Car dealerships offer something to lending institutions that you and I can’t; volume. Generally speaking, car dealerships get access to loans at rates that individual consumers can’t. Dealers then mark up these loans and resell them to customers.
Keep in mind that you don’t have to get your car financed through a dealership. The next time you buy a car, you should consider getting a pre-approval on a loan from another lender. Use this as a comparison for what the dealer is able to quote you.
If you lease a car, dealers have a way to make some profit there too. Dealers make money by marking up the money factor on a lease. The lender charges the dealer a money factor of say, .00125, and the dealer marks it up 50, 75 or even 100 basis points. The difference between the buy rate (what the lender charges the dealer) and the marked up rate (what you’re quoted) is backend profit on the lease for the dealer.
In addition to profit generated from financing or leasing a car, dealers make money from selling different insurance packages or warranties: extended warranties, tire and wheel protection, so on and so forth. With each sale of an additional item, the dealer is making some profit.
Good finance managers are like gold in the car business, and dealerships like to keep them around. Dealerships are also keen to invest in technology and software that increase their F&I margins.
These days, many dealers are investing in third party vendors to make the F&I process more pleasant for the customer. Solutions like docuPAD have been able to make the F&I process easier for the customer while simultaneously increasing the gross profit dealers receive. By empowering the customer to self select which warranties, protections, and plans they want, dealerships are realizing that they are able to sell even more products during the F&I process than ever before.
As a rule of thumb, dealerships can traditionally make much more profit on the backend of a car deal than on the frontend. Depending on the dealership, a “healthy” deal for the car dealer will result in $2,500 to $3,500 in frontend and backend gross profit combined. Remember very little of that will come from the actual sale of the vehicle.
By now you are starting to see how car dealerships truly make their money. Selling cars is simply a means to sell other products and services, and it’s through those other products and services that dealers make their money.
As far as products and services a car dealership has to offer, look no further than their parts and service department for a plethora of options. For all car dealerships, their primary revenue generator (and profit center) is the Parts and Service department.
Let’s start with the Parts department. The parts department at any car dealership keeps in stock a variety of relevant items that go towards fixing, maintaining, or upgrading a vehicle. From tires to shocks, a dealership’s parts department will have hundreds, if not thousands of unique items stocked at any given moment.
The Parts department sells these parts to three customers:
Customer #1 is easy to understand. Let’s say you blow a tire in your Mazda and you show up at the local dealer to get it fixed. The parts department will happily sell you a replacement tire. In this instance, the dealership makes money off of selling you the marked up tire.
Customer #2 is also easy to understand. Let’s use the same example as above. This time, when you get to the dealership, they tell you they don’t have the tire you need. You ask the dealership to call another local dealer and buy the tire from them. In this case, the dealership that sold the tire made some money by selling it to another dealer.
Customer #3 is less obvious to someone who isn’t in the business, but it represents the most common customer of the Parts department; the dealership’s Service department. To keep using our example, instead of buying the tire outright from the dealer, and then going to an independent tire shop, you decide to simply let the dealership mount the new tire for you. In this case, on your invoice you’ll see charges for parts (the tire) and labor (mounting the tire). Yes, you, the customer are still paying for the tire. However, the dealer was able to bundle together the parts and service into one transaction. In these instances, the Service department is “buying” the part from the Parts department, and then charging you, the customer for both the parts and the labor.
The Service department is where car dealerships make most all of their money. In the business there is a concept called “service absorption.” Service absorption is the percentage that the Parts, Service and Body Shop operating gross covers of the total of its own entire combined department operating expenses PLUS the total of fixed expenses and dealer salary.
Car dealers aspire for 100% (or higher) service absorption, although most reach 70%. If a dealer attains 100% service absorption, that means that their Parts, Service, and Body Shop make enough profit to pay for all dealership expenses. Let that sink in for a moment…
How do dealers make money in the Service department then? By beating the book time associated with every vehicle that comes through the service lane.
For a Service department, it doesn’t matter if a vehicle is under warranty or not. Dealers will happily send invoices to manufacturer’s for cars under warranty. What is most important is that their mechanics can beat the book times stipulated for each job.
Auto repairs are charged based on how long a job should take, multiplied by a shop’s hourly rate. If a certain job should take four hours, and a mechanic can get it done in two, guess what the dealer is going to charge you for? Four hours of work. And, they’ll bill you at their hourly rate (which is generally going to be quite high).
This is how car dealerships make their money, by processing repairs, maintenance, and more through their service drive efficiently.
Up to now we’ve covered the traditional ways car dealers make money. There are a few nontraditional ways dealers (and more appropriately, their owners), can make money.
Savvy dealers make money from their dealership by owning the real estate that the dealership sits on. This is another way dealers can make a lot of money. Many dealers own the land they build their dealerships on, and then the dealership pays them rent each month to operate there. In my 42 years in the car business, I’ve seen dealers of all sizes make money from paying themselves rent.
I’m even aware of dealers who have repurposed an existing facility and rented it out to a competitor to sell a different brand. You can’t underestimate the value of the real estate that a dealership sits upon, that land is a veritable gold mine.
So there you have it, those are the myriad ways car dealerships make money.
Q: How do car dealerships make most of their money?
A: Most dealerships make the bulk of their profits from the Finance and Insurance (F&I) department and service and parts operations — not just car sales. While new car sales bring in revenue, the margins are often thin. Extended warranties, loan markups, and service contracts are where profits grow.
Q: Why do dealers mark up interest rates on car loans?
A: Dealers often partner with lenders and are allowed to mark up the buy rate (what the lender offers) to a higher rate for the buyer. The dealer keeps the difference, which can amount to hundreds or thousands of dollars over the life of the loan.
Q: Do dealerships make money on trade-ins?
A: Yes. Sometimes, dealerships appraise trade-ins at wholesale value and resell them at retail value. In other cases, the dealership sells the trade-in at a wholesale auction. The spread between what they pay and what they sell for is a key profit center.
Q: Are add-ons like extended warranties and gap insurance negotiable?
A: Absolutely. Many F&I products are marked up significantly, and dealers often have room to negotiate. You don’t have to buy these products on the spot — you can often find better deals from third-party providers like CarEdge.
Q: What’s the most profitable part of a dealership?
Typically, it’s the service and parts department, followed by F&I. Fixed operations (maintenance, repairs, and warranty work) provide recurring revenue long after the initial sale.

Ready to outsmart the dealerships? Download your 100% free car buying cheat sheets today. From negotiating a deal to leasing a car the smart way, it’s all available for instant download. Get your cheat sheets today!
CarEdge is a trusted resource for car buyers, offering data-backed insights, negotiation tools, and expert guidance to help consumers save time and money. Since 2019, CarEdge has helped hundreds of thousands of drivers navigate the car-buying process with confidence. Learn more at CarEdge.com.
Buying a car is no easy task. Buying a car long distance from a dealer can prove even more challenging. For the average person, what to know when buying a car long distance from a dealer can be confusing and complex. Fortunately it doesn’t have to be.
Let’s discuss why you might find yourself buying a car from a dealer in a different region, what information you need to know, and what steps you should take.
Let’s address the elephant in the room; why would you even want to buy a car from a dealer that’s not in your area? It’s likely that there’s a car dealership within a few miles of where you are right now. Why would you buy a car from someone on the other side of the country?
The simple answer is that the only car you could find that matches all your criteria is somewhere far away. The more complex answer could be that the non-local dealer offered a better price than the one nearby. Or, perhaps the non-local dealer has a car that has been converted into a certified pre-owned vehicle that actually offers a longer warranty than a brand new car (at a lower price).
If you’re thinking about buying a car, you might enjoy this article if you haven’t read it already: How Much Do Dealers Markup Used Cars?
For example, I remember one time when I purchased a 6,000 mile retired service loaner MDX that had been CPO’d. I ended up with a 5 year 60,000 mile bumper to bumper warranty, as opposed to the 4 year 50,000 mile warranty that came with it brand new from the manufacturer. Sometimes looking for cars like this can help you save money while still getting what you want (or more).
There are any number of legitimate reasons to buy a car from a dealer that is far away from you, and these are just a few of the most common.
I can’t say it enough, get any used car that you are buying from a distance inspected by an independent mechanic. Most franchised dealerships do a great job of inspecting and reconditioning their used cars, and you can (and should) ask them for the vehicles inspection and repair records. However, even with this information, it doesn’t hurt to get a pre-purchase inspection completed.
This is especially true if you are purchasing a car from a smaller used car lot. They may also be less willing to share repair orders with you.
How should you go about orchestrating a pre-purchase inspection when you live in California, and you just found your dream car in Idaho? It’s a lot simpler (and dealers are a lot more willing to help) than you might think.
Google is a wonderful tool when it comes to gathering information. This is undoubtedly true when it comes to finding a mechanic to inspect a potential used car purchase. Since you’ve found your car in a different region, it’s unlikely you know a mechanic that you trust to go over to the dealership and inspect it.
My recommendation would be to Google search to locate a qualified mechanic near the dealership to handle your pre-purchase inspection. Call them and let them know your situation (I live in California, and am looking to buy this car that’s near you, can you please inspect it, etc.)
Once you have a mechanic, and a car you would consider buying, make arrangements with the dealer to take the car to your independent mechanic for the pre-purchase inspection for you. Most dealerships will be willing to assist in moving a car from their lot to a mechanic’s shop to conduct the pre-purchase inspection. Don’t be afraid to ask them to do this.
I do have one note of caution with pre-purchase inspections. Your mechanic will find something wrong with the car. At the end of their day, it’s their job to find something. It could be something minor, it could be a little nit picky, it could be something that you need to take care of ASAP before you buy the car, just keep in mind that they will find something.
Do you go and pick it up? Do you get the car shipped to you? How the heck do you actually get the car you want to buy from a long distance dealer into your garage at home?
This is a matter of personal preference, and how much time (and money) you can set aside for such an endeavor.
If you’re thinking about buying a car, you might enjoy this article if you haven’t read it already: Monroney Sticker & Window Sticker Explained by a Former Car Dealer
During my 42 year career in the business, I had customers who travelled great distances by train and plane in order to pick up their new car to simply have the joy of driving it home. By great distances, we’re talking about several hundred, even up to a 1000 miles.
I also had customers who purchased a car from afar and made arrangements to have it shipped to them. For them, the “thrill” of driving hundreds of miles back home wasn’t worth the time it would take to get to the dealership and back. Many of my customer’s worked with Ship a Car Direct to get their cars delivered to them.
Those are your two options. If you’re unsure how to navigate this process consider letting us help. At CarEdge we’ll help you navigate the car buying process.
More and more dealerships are making it easier for you to purchase a car online. As the industry transitions from physical sales to ecommerce, there are bound to be changes in how people buy their cars.
One of the most popular tools that dealerships are using today to help with online sales comes from a company called Roadster. Roadster allows customers to seamlessly complete the entire purchase online. From inquiring about a particular car, to starting and completing the paperwork process, to making arrangements for shipping so that you never have to step foot into the dealership, Roadster provides the software to make it happen.
You could live in Seattle, purchase a specific Lexus that you found at a dealer in Pennsylvania, and do it all from the comfort of your home or office. The business model for how cars are being sold is changing dramatically. As someone once said, “it’s a small world, but I wouldn’t want to have to paint it.”
Keep in mind what we discussed above. What you need to know when buying a car long distance from a dealer isn’t as complex or challenging as you may have thought. Yes, there are a few more considerations, but they certainly aren’t insurmountable.
When it comes to cars, there’s a lot of jargon. So much so, that the already confusing process of buying a car, can get even more challenging for someone who isn’t well versed in automotive lingo. Throw in terms like monroney sticker, window sticker, and more on top of an already confusing subject matter, and you’re bound for frustration.
Fortunately, as with most things in life, these words and phrases aren’t actually as complex as they seem. Feeling confident when you buy a car is a must, and knowing the key words, phrases, and jargon that the dealer may throw around is a necessary step in that process.
Let’s explain the two terms above, the Monroney label, and the window sticker. Fortunately for you (as you’ll see in a moment), the two phrases refer to the same thing!
This is a loaded question, but we have to ask it… Do you trust your average car salesperson?
Odds are, you don’t. When asked, “Rate the honesty and ethical standards of people in these different fields — very high, high, average, low or very low?” Gallup found that only 9% of Americans identify car salesmen as having a “high” or “very high” level of ethical standards. This was by far the lowest rating of all professions (even below “Members of Congress”). Ouch.
If you’re thinking about buying a car, you might enjoy this article if you haven’t read it already: How Much Do Dealers Markup Used Cars?
Why is this important? Because it is the entire reason Monroney stickers exist. A car’s Monroney sticker presents all of the features, options, and charges associated with every single new car in the United States. Before the Monroney sticker existed, customers had to trust the salesperson at the dealership to provide them with information about what a car included, and how much it cost. The Monroney sticker made that information accessible (and mandatory) for all new cars.
The Monroney sticker applies to all new cars sold in the United States. You’ll frequently also hear it referred to as a car’s window sticker. The two terms are synonymous.
Included on the Monroney sticker are key pieces of information. They include:
As you can see, there is a lot of relevant information packed on the Monroney sticker, and again, with good reason!
I remember the days before Monroney stickers existed… There was a time when Monroney stickers were only mandated for cars and not trucks. It really was like the wild west.
Who, or what is Monroney, and why is their name associated with all new cars sold in the United States? Oklahoma Senator Almer Stillwell “Mike” Monroney sponsored a bill called the Automobile Information Disclosure Act of 1958. This bill would lead to the creation of the Monroney sticker once it was signed into law by then president Dwight Eisenhower.
Monroney was a pioneer for consumer safety. He also sponsored the bill that would eventually create the Federal Aviation Administration.
More in depth information on the legislation Monroney pursued can be found here: https://www.justice.gov/civil/consumer-protection-branch-32
As mentioned above, Monroney, or window stickers are required to have the following information:
Dealers are not permitted to remove, modify or alter these stickers in advance of selling a car.
Now that you know that a window sticker is required by law on all new cars in the United States, you’ll certainly be looking for it during your next dealership visit. Edmunds.com provides a great overview of where to look for each piece of information on the window sticker. Click here to view that article.

Ready to outsmart the dealerships? Download your 100% free car buying cheat sheets today. From negotiating a deal to leasing a car the smart way, it’s all available for instant download. Get your cheat sheets today!